Special education teacher responsibilities include creating and implementing Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) and adapting lessons to meet diverse learning needs. They also provide direct instruction and individualized support to students.
Special Education Teacher
As a special educator, understanding special education teacher responsibilities is vital.
Whether you’re a seasoned pro, a teacher just stepping into this role, or an administrator building a team, you’ll find value in this overview of what the job really requires.
These responsibilities shape how students with disabilities access learning, how inclusive classrooms function, and how we ensure every learner thrives.

What Are Special Education Teacher Responsibilities?
A key part of a teacher’s job is delivering instruction. But when we talk about special education teacher responsibilities, the role is broader.
It means working with students who have identified disabilities, adapting general‐education lessons, providing individualized instruction, and operating in inclusive settings, resource rooms or self‐contained classes.
Must assess skills, determine educational needs, and tailor instruction accordingly.
Core Special Education Teacher Responsibilities & Duties
Here are the main duties you’ll encounter:
- IEP development and implementation: designing Individualized Education Programs, setting goals, arranging accommodations.
- Instructional planning & curriculum adaptation: modifying lessons, using assistive technology, differentiating instruction.
- Assessment, progress monitoring & data tracking: formal/informal assessments, tracking IEP goals, revising plans based on student performance.
- Behavior supports & classroom management: implementing behavior intervention plans (BIPs), creating positive learning environments.
- Collaboration with team, families & therapists: co-teaching, coordinating with general educators, speech/occupational therapists, engaging parents.
- Legal compliance & documentation: meeting timelines, maintaining records, following IDEA/FERPA rules.
These duties reflect the full spectrum of special education teacher tasks and job duties in today’s inclusive schools.

Skills & Qualifications for Special Education Teachers
| Skill / Qualification | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| State licensure in Special Education | Ensures teachers meet required professional standards |
| Assessment knowledge | Guides IEP goals and instructional decisions |
| Assistive technology skills | Improves accessibility and student engagement |
| Co-teaching & collaboration | Supports inclusion and unified instruction |
| Differentiated instruction expertise | Meets diverse learning needs effectively |
| Patience & empathy | Builds trust and supports emotional needs |
| Strong communication skills | Enhances family partnerships and teamwork |
| Problem-solving abilities | Helps respond to challenges quickly and creatively |
| Adaptability & flexibility | Allows teachers to adjust to changing student need. |
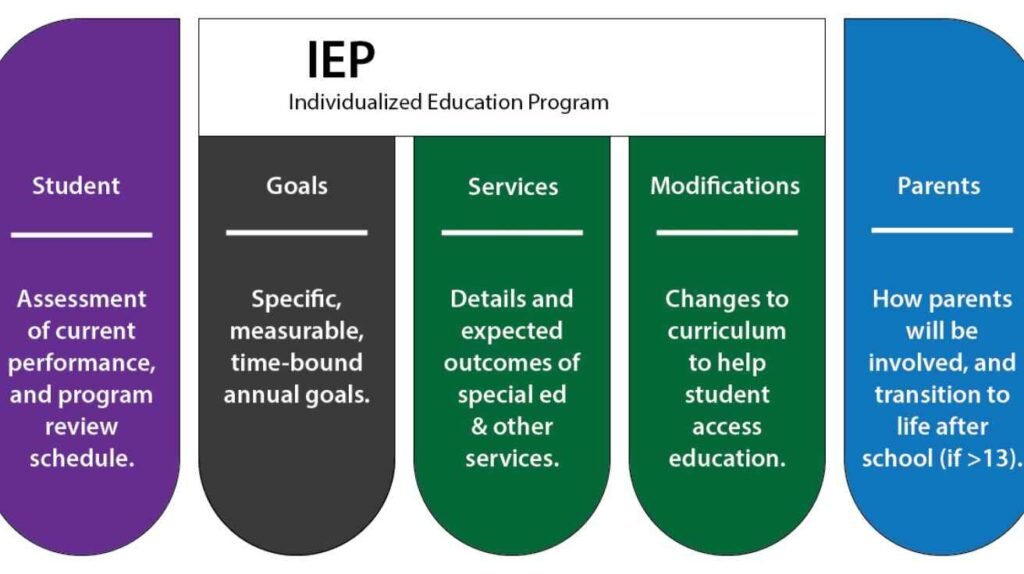
IEP Responsibilities & Case Management
IEPs is a central part of the special education teacher role.
Among the most critical responsibilities: managing IEPs. You act as the case manager, leading IEP meetings, assessing student performance, writing goals, and monitoring progress. An IEP is more than a plan — it’s the roadmap for what each student needs to succeed.
You collaborate with general education teachers, therapists, parents, and administrators. You also use assessment data to decide if goals or accommodations need adjustment.
Individualized Instruction & Curriculum Adaptation
One of the core special education teacher responsibilities is providing individualized instruction. This is the heart of the special education teacher job description.
This means – tailoring lessons to each student’s strengths and needs, applying scaffolding, and using assistive technology to bridge gaps.
In an inclusive classroom or when co-teaching, you adapt the general education curriculum, provide accommodations versus modifications, and ensure every student has access.
Behavior Management & Support Plans
Behavior is often tightly linked to learning. So part of your responsibility is supporting behavior through Behavior Intervention Plans (BIPs) and positive behavior strategies.
You create a structured environment, teach routines, and collaborate with behavior specialists. This aspect of the role ensures that students don’t just learn academic content but also thrive socially and emotionally.
Assessment, Progress Monitoring & Reporting
Regular assessments—formal tests, observations, informal check-ins—help you monitor student growth.
Track this data against IEP goals and refine instruction accordingly. Reporting that progress to families and team members completes the cycle. Accurate data collection and clear communication are key parts of the special education teacher responsibilities list.
| Task | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Lesson planning & adaptation | Tailor learning to student needs |
| Co-teaching | Support inclusion and access to curriculum |
| Small-group / 1:1 instruction | Strengthen targeted skills |
| IEP meetings | Review goals and accommodations |
| Collaboration with therapists | Coordinate essential student supports |
| Progress monitoring | Track growth and adjust instruction |
| Parent communication | Maintain strong home-school connection |
| Behavior support | Promote positive learning environments |
| Documentation | Meet legal and program requirements |
Collaboration With Teachers, Therapists & Families
Collaboration is one of the most important parts of effective special education.
Your role isn’t solo. You partner with general education teachers, therapists (speech, occupational, physical), teaching assistants, and you engage families as advocates and partners.
This ensures that accommodations and specialized supports are understood and executed in all settings.

Legal Compliance & Documentation Duties
Every special education program is governed by laws and regulations.
You must ensure compliance with the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) and other guidelines: documentation of eligibility, IEP timelines, reevaluations, and confidentiality under Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA).
This legal framework forms the backbone of your responsibilities around accountability and documentation
Resources & Tools to Support
Helpful tools include: IEP-management software, progress-monitoring apps, assistive technology (text-to-speech, adaptive keyboards), and specialist organizations that offer training and communities of practice.
These support your ability to meet your special education teacher duties with confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What are the most important special education teacher responsibilities?
A: The most important responsibilities include developing and implementing IEPs, providing individualized instruction, monitoring progress, adapting curriculum, collaborating broadly, and managing behavior supports.
Q2: What does a special education teacher do every day?
A: Daily tasks typically include lesson planning and adaptation, small-group or one-on-one instruction, co-teaching, tracking student data, meeting with therapists or parents, and updating documentation.
Q3: Why is collaboration important for special education teachers?
A: Collaboration ensures consistent support across settings: between general and special education teachers, therapists, aides and families—leading to successful inclusive education.
References
Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor. (2025, August 28). Special education teachers. https://www.bls.gov/ooh/education-training-and-library/special-education-teachers.htmBureau of Labor Statistics
Workable. (n.d.). Special education teacher job description. https://resources.workable.com/special-education-teacher-job-description













